The structure of education
The system is based on:
- Division of course programmes in line with the BMD model: Bachelor’s degree (Bac+3), Master’s (Bac+5) and Doctorate (Bac+8)
- Division of courses into semesters (1 year = 2 semesters);
- Organisation of courses into compulsory, optional or free-elective course units, including formal lectures, directed studies and practical work, internships, dissertations, etc.;
- Recognition of students’ progress and work completed through the award of ECTS credits (European Credit Transfer System). Each course unit corresponds to a specified number of ECTS credits, and one validated semester corresponds to 30 ECTS credits.
The types of institutions
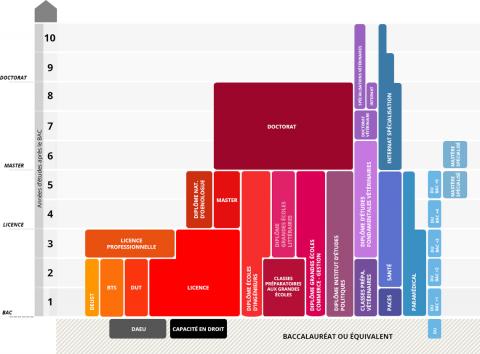
The French higher education system includes several types of institutions:
- Universities offer courses in many fields (art, literature, languages, humanities and social sciences, health, science and technology, etc.);
- Schools: engineering, commerce, architecture, veterinary, agronomy, etc.;
- High schools also dispense some higher education courses: BTS (technical diploma), CPGE (preparatory classes for the Grandes écoles), etc.
The University of Toulouse brings together 22 institutions, delivering 900 degrees. > Explore this multifaceted course offering!
Learn more about higher education in France on the website of the French Ministry of Higher Education, Research and Innovatio




